What t-test to use: Student’s or Welch’s?
The VSNi Team
13 June 2022
Imagine we are interested in whether female undergraduate students with blonde or brown hair have different heights, on average. To investigate this, we randomly sample blonde and brown haired female undergraduate students and measure their height.
Our hypothesis test
=
≠
Test assumptions
| Assumptions | Student’s t-test | Welch’s t-test |
| Two independent, random samples |  |  |
| The two populations have Normal distributions |  |  |
| The variances of the two populations are equal |  |  |
Sample size consideration
If the sample sizes are unequal between the two groups, Welch's t-test performs better than Student's t-test.
What test to use?
| If you have | Use |
| Unequal sample variances and/or unequal sample sizes | Welch's t-test (also known as the unequal variances t-test) performs better (i.e., is more reliable) than Student’s t-test |
| Equal population variances and equal sample sizes | Student's t-test has more power than Welch's t-test |
Performing the test in Genstat
Performing a Student’s t-test or Welch’s t-test in Genstat is straightforward.
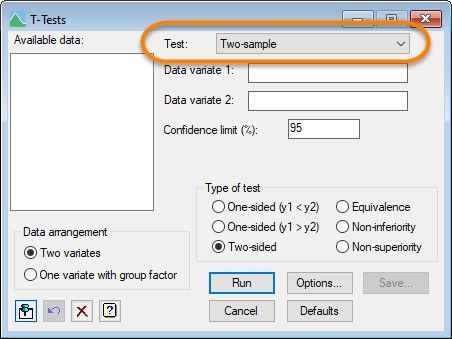
From the menu bar, select Stats | Statistical tests | One- and two-sample t-tests. Then, in the T-Tests menu, set the type of test to Two-sample.
Running a Student’s t-test in Genstat
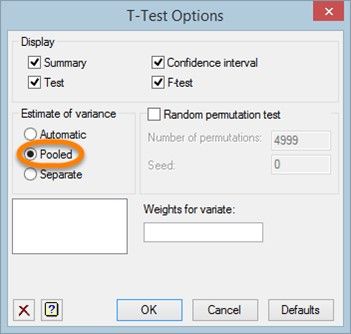
We can run a Student’s t-test by clicking the Options button, then selecting Pooled as the method used to estimate the variances for the test.
Running a Welch’s t-test in Genstat
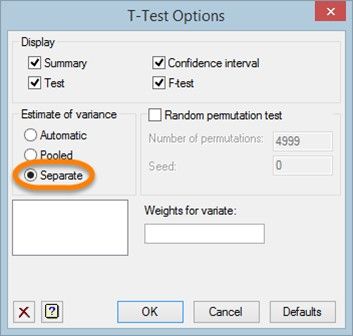
To run a Welch’s t-test, in the T-Test Options menu select Separate as the method used to estimate the variances for the test.
Popular
Related Reads